Abstract
Subject content knowledge (SCK) and pedagogical content knowledge (PCK) are key components of teacher competence that affect teaching and students’ learning and thinking about the future. In this study, SCK and PCK were analyzed from Finnish and Spanish (n = 360) primary school student teachers’ (PSTs) answers using a questionnaire that included environmental problems and teaching sustainability. The answers were analyzed with theoretically guided deductive and inductive content analyses. The PSTs considered it important to teach factual, conceptual, methodological and metacognitive knowledge and skills for solving local, regional and global environmental problems. Critical and evaluative knowledge also appeared, but in rather few answers. The results are discussed regarding the meaning of SCK and PCK and a powerful knowledge of science disciplines, such as biology and the geosciences.
License
This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Article Type: Research Article
INTERDISCIP J ENV SCI ED, Volume 21, Issue 4, 2025, Article No: e2520
https://doi.org/10.29333/ijese/17442
Publication date: 19 Nov 2025
Article Views: 937
Article Downloads: 337
Open Access HTML Content Download XML References How to cite this articleHTML Content
INTRODUCTION
Teachers’ pedagogical choices are decisively important to what is learned and how it is learned (Burroughs et al., 2019; Hattie, 2011). Thus, the quality of the learning opportunities created by teachers affects students’ learning and motivation (Lutovac & Körkkö, 2024). A teacher’s knowledge of a given subject matter is particularly important to students’ progress (Laghari et al., 2023), which is perceived as key to a teacher’s competence (Kleickmann et al., 2017). Teacher’s knowledge focuses, among others, on two main constructs: subject content knowledge (SCK), i.e., domain-specific subject matter knowledge and pedagogical content knowledge (PCK) (Rosenkränzer et al., 2016; Shulman, 1987). Although the definitions of these concepts vary across researchers (Kleickmann et al., 2013; Sarkar et al., 2024), there seems to be a consensus on some crucial aspects.
SCK represents teachers’ understanding of the subject matter being taught, whereas PCK is the knowledge needed to make a subject matter accessible to students (Shulman, 1986). Thus, PCK is the application of pedagogical theories to a discipline or a subject context. It has two core facets: knowledge about students’ subject-specific conceptions and misconceptions and knowledge about subject-specific teaching strategies and representations (Park & Oliver, 2008).
Despite the clear theoretical distinction between SCK and PCK, findings on their empirical separability are mixed (Kleickmann et al., 2013). Previous studies have shown that student teachers’ knowledge and understanding of core concepts and processes, e.g., in ecology (Palmberg et al., 2016; Yli-Panula et al., 2017), and of teaching strategies and methods are poor (Yli-Panula et al., 2017). Furthermore, SCK in biology, for example, is increasing rapidly, which requires new teaching methods to support learners’ abilities to evaluate, conceptualize and update their knowledge and skills.
To develop the PCK of teacher education programs, it is important to know what kind of knowledge of student teachers SCK and PCK have and what kind of misunderstandings and deficiencies student teachers have because these views affect the learning of new issues and the construction of new knowledge and action (Valverde-Pérez et al. 2022).
THEORETICAL BACKGROUND
Subject Content Knowledge, Curricular Knowledge, and Pedagogical Content Knowledge
According to Shulman (1986), teachers’ knowledge includes SCK, curricular knowledge, and PCK. SCK ‘refers to the amount and organization of knowledge per se in the mind of the teacher’ (Shulman, 1986, p. 9) and requires an understanding of both substantive and syntactic structures of a discipline (Schwab, 1978). Thus, SCK refers to subject matter’s such as facts, specific details or elements and concepts. Concepts again include the relationships between basic elements, principles, generalizations or theories (Krathwohl, 2002). To teach a subject, one must know its facts, concepts, theories, how to organize its principles and structures and rules for establishing what is legitimate to do and say in a subject-specific teaching area (Shulman, 1986), for example in biology education.
Shulman (1986) conceptualized teachers as the medium through which students experience the content of the curriculum. Curricular knowledge includes
understandings about the curricular alternatives available for instruction … familiar[ity] with the curriculum materials under study by his or her students in other subjects they are studying at the same time … [and] familiarity with the topics and issues that have been and will be taught in the same subject area during the and later years in school, and the materials that embody them (Shulman, 1986, p. 10).
PCK refers to the character of content knowledge needed for the practice of teaching. Shulman (1986) defined PCK as the knowledge of content that informs ‘the ways of representing and formulating the subject that make it comprehensible to others’ (p. 6). Additionally, Shulman (1987) described PCK as ‘that special amalgam of content and pedagogy that is uniquely the province of teachers, their own special form of professional understanding’ (p. 8). Thus, PCK involves transforming one’s content knowledge into curricular material and pedagogical representations. For Shulman (1986, p. 9), it is ‘the most useful forms of [content] representation ..., the most powerful analogies, illustrations, examples, explanations and demonstrations–in a word, the ways of representing and formulating the subject that makes it comprehensible for others’.
Later, Shulman (1987, p. 8) stated that teachers’ knowledge includes seven approaches:
-
content knowledge (knowledge of a particular subject),
-
curricular knowledge (the materials and programs that serve as ‘tools of the trade’ for a teacher),
-
general pedagogical knowledge (broad principles and strategies of classroom management and organization that appear to transcend the subject matter),
-
knowledge about learners and their characteristics,
-
knowledge about educational contexts (ranging from the workings of the groups or class and the governance and financing of school districts to the character of communities and cultures),
-
knowledge about educational ends, purposes and values, and their philosophical and historical grounds, and
-
PCK (the special content and pedagogy, that is the subject teacher’s own special form of professional understanding).
Shulman (1986, 1987) also discussed how different types of knowledge relate to SCK and PCK (see Table 1).
Table 1. Knowledge categories and types (Gudmundsdottir & Shulman, 1987; Shulman 1986, 1987)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Teachers should have competencies that serve SCK and all aspects of PCK of the subjects that they teach. These teacher competencies are the knowledge and skills that a teacher can use to support students’ learning in a complex school environment where critical decisions are required every day (García-Fortes et al., 2024). They refer to the knowledge, skills, attitudes, values and personal qualities that enable professional and effective action in teaching and learning situations (Koster & Dengerink, 2008).
In general, the concept of competence is understood as the individual’s self-developed ability, skill, desire and will to make use of their own scientific expertise and experience in making decisions and in action (Sjöström & Eilks, 2018). Features that support the effective realization of PCK are knowledge about action that reflects the teacher’s actions. The former means that the teacher combines different components of PCK in the teaching situation to create teaching that is meaningful for the students. The latter means that the teacher must expand or modify the teaching of a certain subject by modifying his or her own PCK.
Powerful Knowledge as Part of SCK and PCK
According to Young et al. (2014, p. 74), knowledge is powerful if it predicts, explains and enables individuals to envisage alternatives. Building on this, they provide three distinctions, or criteria, for ‘powerful knowledge’: It is systematic, specialized and distinct from the ‘common sense’ knowledge acquired through everyday life. Powerful knowledge originates from an academic discipline or discipline that is transformed into a school curriculum (Dempster, 2023; Muller & Young, 2019). This forms the basis for making knowledge-based generalizations and evaluating teaching and learning processes. It can enable students to acquire knowledge that takes them beyond their own experiences (Young et al., 2014). For example, it links environmental facts to concepts that can themselves be linked to broader concepts and theories.
Understanding and solving environmental problems requires both SCK and PCK related to planetary boundaries (Rockström & Sukhdev, 2016). Planetary boundaries are boundary values that define a safe area of operation for humanity within the framework of biological and physical systems (Rockström et al., 2009). Powerful knowledge has transformative power and is connected to transformative teaching and learning because students can reconcile their new observations into existing concepts, make conceptual connections, gain insights into their observations and generate ideas (Muller & Young, 2019).
Biology and geoscience are essential subjects when teaching environmental issues from the perspective of sustainability education (SE). Because they are taught both in Finland and Spain, powerful knowledge in this study is focused on from the perspectives of these subjects (Finnish National Board of Education [FNBE], 2016; LOMLOE, 2020).
Environmental Issues and Sustainability Education
Human activity causes several environmental problems locally, regionally and globally. To prevent irreversible changes, European countries strive to promote environmental policy and are therefore considered pioneers in sustainability issues (European Parliament, 2023). However, this policy is not quite ready to achieve all its goals. Greenhouse gas emissions, waste generation, material consumption, the intensity of forest use and nutrient pollution must also be reduced more effectively than at present (OECD, 2021), albeit daily behavior seems to reveal increased individualism and a decreased sense of community. Many of today’s environmental challenges require a veritable shift in thought and behavior to support sustainable living. According to Sterling (2008), necessary change can be achieved through SE. Sterling (2008) defines the concept as follows:
a change in educational culture, one which develops and embodies the theory and practice of sustainability in a way which is critically aware. It is therefore a transformative paradigm which values, sustains and realizes human potential in relation to the need to attain and sustain social, economic and ecological wellbeing, recognizing that they must be part of the same dynamic (p. 22).
Over the years, SE has expanded from the original ecological perspective to include social, ethical and transformative aspects of sustainability (Jeronen, 2023) with the goal of finding sustainable solutions to environmental, social and economic problems through education (Prabakaran, 2020).
According to Palmberg et al. (2015, 2016), student teachers have major gaps in their knowledge and skills in teaching the natural sciences and environmental issues. These results differ from Fitriah et al.’s (2018) regarding SCK and, partly, PCK. According to them, pre-service biology teachers had a good understanding of SCK. They also mastered part of PCK, such as a knowledge of learning strategies and materials, communication with learners and assessment and evaluation. Conversely, pre-service student teachers had difficulties regarding PCK in the following areas: knowledge of curricular development, knowledge about learners and knowledge about developing learners’ potential, in line with Palmberg et al. (2015, 2016). They seem to need education regarding class management, curriculum understanding and recognizing the characteristics and potential of learners.
This study developed as part of the project (teacher student selection–proactive future work), for which a conceptual framework was developed for teaching quality in the form of a multidimensional adapted process model of teaching. The theoretical basis of the project was Blömeke et al.’s (2015) model, which depicts teacher competences as a continuum where dispositions (e.g., teacher knowledge) are dynamically interlinked with observable job performance (e.g., quality of instruction). Blömeke et al.’s (2015) model was developed further in several ways. These modifications of and novel contributions to the competence model are described in detail in the article Metsäpelto et al. (2022).
Since teacher education plays an important role in these issues and research results vary, more research is needed. Based on the previous ideas, we conducted a survey expecting to fill an important research gap by investigating future primary school teachers’ views of SCK and PCK in biology and the geosciences related to environmental issues. The purpose of this study is to investigate future primary school teachers’ views on the key issues, concepts and environmental problems that should be taught in biology and the geosciences and their views regarding teaching-related skills. This work may reveal possible misunderstandings and deficiencies so their teaching can be considered within education programs. The following research questions (RQs) guided this study:
RQ1. What kind of SCK do the primary school student teachers’ (PSTs) responses contain regarding:
-
essential factual and conceptual knowledge in biology and geoscience?
-
key local, regional and global environmental problems?
RQ2. What kind of PCK do in the PSTs’ responses contain regarding methodological, metacognitive, evaluative, critical and reflective knowledge:
-
of the essential skills to be taught?
-
of key local, regional and global environmental issues?
With the first RQ, we want to investigate the perceptions of PSTs about what SCK they have; whereas the second question provides answers to how they understand PCK.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Participants
The data of this study were collected in 2020-2021. In total, 360 second-year PSTs participated in the survey as volunteers: 190 Finnish primary school student teachers (FPSTs) and 170 Spanish primary school student teachers (SPSTs). Most PSTs (over 80%) were women, and 71% of PSTs were 20-24 years old (the mean age was 21.32 years, standard deviation = 9.9). The respondents were second-year PSTs with similar studies in teacher education. All the students had observational experience from their first teaching practice in schools, but no teaching experience. Participants from both countries were selected based on convenience sampling due to their accessibility and availability for the study. In addition, it is important to notice that countries’ results will not be compared. The results concerning the FPSTs’ and SPSTs’ SCK and PCK will be used in the development of biology and geoscience curricula.
Data Collection
The web-based (Webropol) survey was administered according to the rules of the ethics committee of each university. It was piloted with a group of subject student teachers from each country. The questionnaire contained, among others, the following two questions:
Q1. What skills and knowledge related to sustainable development do you consider essential to teach in primary school?
Q2. In your opinion, what are the most essential environmental problems? How would you try to solve these problems
-
locally,
-
regionally or
-
globally? Comment on each part of this question.
The number of PSTs’ answers varied between the open-ended questions. More than two-thirds of the PSTs answered the questions. Approximately 82% of the FPSTs and 89% of the SPSTs answered essential skills and knowledge to be taught (Q1). On average, approximately 83% of FPSTs and 82% of SPSTs answered environmental problems and their solving (Q2).
Data Treatment
As a background to the analyses of the wide-ranging content topics, there are the following issues. The answers to Q1, ‘skills and knowledge’, are expected to be deeply related to teaching and learning. The answers to Q2, ‘environmental problems and how to solve them’, are expected to be based on a knowledge of the natural sciences (e.g., climate change in planetary boundaries, biodiversity conservation or recycling of energy and material cycles on the earth) and, furthermore, the social sciences due to the nature of socio-scientific issues, as well as the answers to ‘with whom’ do you solve them.
In this paper, we used an inductive and deductive approach (Newman, 2000). Thus, PSTs’ answers were analyzed using theory-guided deductive content analyses based on Shulman (1986, 1987). Inductive content analyses were used following their common procedure (Krippendorff, 2013; Tuomi & Sarajärvi, 2018). First, three researchers familiarized themselves with the material by reading the answers; subsequently, similarities and differences in PSTs’ expressions were listed, followed by identifying issues in the responses according to the established categories based on Shulman (1986, 1987). The categories were adapted to our data to conclude the final classification of the answers (Table 2).
Table 2. Theory-guided categories, definitions and examples related to SCK and PCK, modified for this study
|
There were difficulties when categorizing factual and conceptual knowledge because many answers included, for example, a list of facts or very short statements that did not explain the issue very much. Factual and conceptual knowledge were analyzed in connection with environmental problems, and they are presented together in this article. Moreover, critical and reflective knowledge is presented together since they appeared closely related in PSTs’ answers.
Furthermore, categorization of the PCK was conducted regarding PSTs’ methodological, evaluation, critical thinking and metacognitive knowledge.
To ensure the reliable assignment of the analytic categories in these open-ended questions, Cohen’s kappa as an agreement measures interrater reliability for categorical data and was calculated based on the total independent coding of three researchers. The results show substantial agreement (κ = 0.72), according to Landis and Koch (1977).
Although Finnish and Spanish results are presented separately, the main focus is the phenomenon. Countries’ results should not be compared; rather, the SCK and PCK analyses should be compared when the PSTs state that they consider the essential skills and knowledge to be taught in primary school, the most important existing environmental problems and their solutions.
RESULTS
Frequency of SCK and PCK in Finnish and Spanish PSTs’ Answers
Both SCK and PCK appeared in PSTs’ answers concerning essential skills and knowledge for primary school (Q1) and in local, regional and global environmental problems (Q2). Regarding the latter, the most often there appeared to be factual and conceptual knowledge concerning environmental problems. Approximately 90% of PSTs’ answers included factual or conceptual knowledge regarding environmental problems, and approximately 80% of answers concerned essential skills and knowledge regarding sustainable development (see Figure 1). Methodological knowledge appeared in approximately half of the answers (FPSTs 66%, SPSTs 41%). Metacognitive knowledge appeared less frequently and varied widely in the answers between the questions, being the highest on answers concerning essential skills and knowledge for both the FPSTs and SPSTs. Evaluative, critical and reflective knowledge appeared at a very low frequency, above all among the SPSTs.
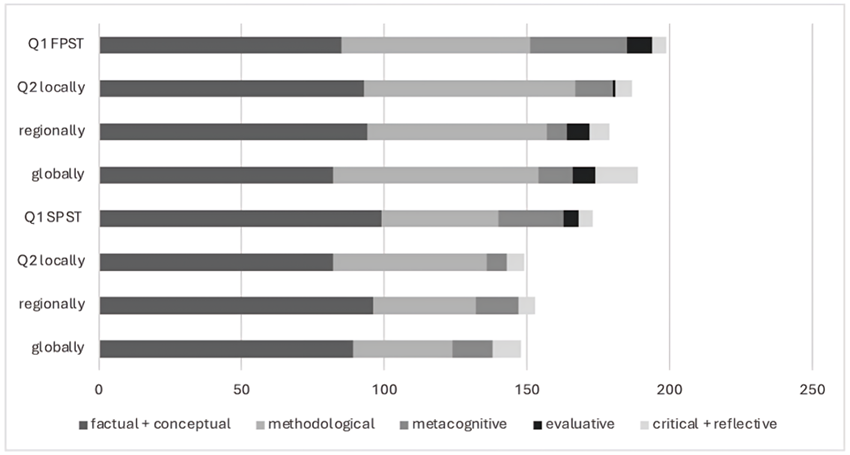
Factual and Conceptual Content Knowledge About the Essential Skills and Knowledge to Teach in Primary School
In PSTs’ answers, the idea appeared that, in primary school, it would be good to start with the very basics, deal with the subject as clearly as possible and highlight opportunities that students can already do. The basics, such as everyday choices, were also regarded as key skills and knowledge to be taught and were regarded as influencing students’ learning. Issues such as teaching theoretical information and developing students’ relationships with nature appeared, as well as understanding the meaning of nature as a key means and content of SE in primary school.
Factual and conceptual knowledge-related issues comprised most results (FPSTs 94%, SPSTs 99%), which were usually connected to ecological sustainability.
“One example of the list was recycling, renewable natural resources and biodiversity” (SPST103).
Some PSTs brought up factual knowledge in slightly more sophisticated sentences by mentioning concepts concerning sustainable development. For example, FPST69 wrote the following:
“Economic and social sustainability.”
FPST69 further explained,
“Because the economy is strongly linked to nature and social sustainability, it is important, because young people worry about climate issues.”
Factual and Conceptual Content Knowledge About Key Environmental Problems Locally, Regionally and Globally
Factual and conceptual knowledge appeared in approximately 90% of PSTs’ answers regarding local, regional and global environmental problems (Figure 1). The most often mentioned factual and conceptual knowledge about local environmental problems was littering, plastic waste recycling, global warming and overconsumption. Moreover, traffic jams, noise, sewage, high carbon footprints, the eutrophication of lakes, clear cutting forests, fragmentation of natural areas and meat production were mentioned. For example, SPST43 wrote the following:
“The river pollution of my city. I would involve the city council to control and sanction, and I’d raise awareness among citizens.”
The connection to school was also mentioned as a lack of enabling recycling opportunities in general and in schools (an awareness and an encouragement of recycling) and in connection to students and PSTs’ own lives, such as cycling opportunities, green and recreation areas, the relationship with nature and efficient public transportation.
Most PSTs’ responses contained factual and conceptual environmental knowledge about regional environmental problems. The issues that appeared in their answers were recycling, littering and pollution, biodiversity and preventing global warming based on leaders’ decisions. This is well illustrated by the following view:
“Diminishing biodiversity. Humans are a significant threat to biodiversity. So, the solution is for people to reflect on their own activities in nature and in everyday life, that is, for example, protecting endangered organisms and animals, for example by avoiding imported meat or protecting forest growth” (FPST17).
Regarding factual and conceptual knowledge about global environmental problems, the PSTs usually mention global warming, littering of all kinds, especially plastic waste, overconsumption and biodiversity. They brought up issues related to the economy, and some PSTs considered the prospect of fossil fuels, the amount/quality of waste and natural loss (i.e., rainforests and barrier reefs). An example of an answer that includes both factual and conceptual knowledge is:
“Stopping and reducing global warming by 1.5 degrees. I vote and support influencers and decision makers who push the issue forward alone. Telling other people and emphasizing will get more votes” (SPST89).
Methodological and Metacognitive Content Knowledge Regarding Essential Skills and the Knowledge for Teaching in Primary School
The PSTs mentioned that the teacher should give examples to the students, act or teach in such a way that the students are not anxious or connect the matter to students’ everyday lives. They also paid attention to ways of presenting and handling the topic being taught.
Methodological knowledge appeared in FPSTs’ and SPSTs’ answers related to essential skills and knowledge in 66% and 41% of answers, respectively. Some PSTs justified the importance of methodological knowledge in teaching recycling because, besides its simplicity, it directly relates to students’ experiential learning. They wrote, for example,
“By teaching small things related to everyday choices, you can directly contribute to sustainable development by bringing it closer to children and making it easier for them to implement” (FPST94).
Metacognitive knowledge appeared in the FPSTs’ and SPSTs’ answers related to essential skills and knowledge in 34% and 23%, respectively. In these answers, attitudes and values were brought up together with the issue (e.g., consumption) to be taught. For example, SPST151 wrote the following:
“It’s essential to teach skills and knowledge related to problem solving in the school context, eliminate all types of discrimination, learn to take care of the planet, reflect on which actions are the most sustainable, practice them more and learn values and attitudes that involve our own well-being and that of the entire society.”
Some PSTs described how they processed, acquired, used knowledge or presented an opinion, such as FPST29’s case:
“In elementary school, it is not appropriate to focus on overly complicated and stressful matters that pupils cannot influence and may only be anxious about the overwhelming nature of the subject. It is expedient to raise awareness.”
Sometimes, PSTs’ answers contained both methodological knowledge and metacognitive knowledge, such as
“Finding connections and understanding an entity. To an individual, throwing one piece of trash on the ground or buying a new piece of clothing may seem insignificantly small, but in the grand scheme of things, when everyone thinks this way, it becomes a problem” (SPST2).
Methodological and Metacognitive Content Knowledge Regarding Key Environmental Problems Locally, Regionally and Globally
Methodological knowledge was presented around a mean of 67% and 41% of FPSTs’ and SPSTs’ answers, respectively, concerning local, regional and global environmental problems (Table 2). Metacognitive knowledge appeared very seldom (less than 15% of answers).
In local environmental problems, both aspects, teaching and learning in school as well as methods concerning the environmental facts, appeared in PSTs’ answers. Subject matter-related methods were also highlighted in PSTs’ answers, such as lowering the prices of sustainable food, a preference for local food with a smaller carbon footprint, refurbishing clothes, minimizing factory emissions in municipal politics etc. The PSTs highlighted reflections with the students as one of their main teaching and learning methods:
“You can reflect with the student on what kind of consumption culture you have” (FPST160).
Alternatively,
“Agreeing on rules in school with the students, project work, working with colleagues to get the active learning methods to school, for example to inhibit littering, practicing in class what sustainable products are or encouraging the reduction of consumption” (SPST125).
Regionally, methodological knowledge appeared similarly to answers concerning local problems. For example, SPST33 wrote about the eutrophication problem of Mar Menor:
“I would make my students aware of the great importance of this place and the problems it is going through, so that the entire population, from a young age, is made aware of the importance of taking care of their environment and being responsible with their actions.”
Global mentions can refer to methods such as the climate agreement, reducing electricity and water, imparting knowledge and teaching about issues and restricting emissions to apply to the countries that produce the most.
“In most cases, a precise method for how to do this was not really mentioned, only the term climate agreement” (SPST4).
Evaluative, Critical and Reflective Content Knowledge About Essential Skills and Knowledge to Teach at Primary Schools
A few answers (FPSTs 9%, SPSTs 5%) appeared regarding evaluative knowledge (Figure 1). Only in one answer did the evaluative information focus on teaching-related phenomena, such as teaching methods. In other answers, evaluative knowledge was targeted to behavior, nature–environment observations, the media issues, students’ actual need for goods, students’ choices, students’ opportunities to act or the correctness of information.
The following answer relates to teaching and human skills and represents evaluative and critical knowledge (FPST87):
“One of the most important ecological skills is optimism. Through this, I would look for answers to basic questions, such as: How can the human attitude towards climate change be critical and hopeful at the same time? What can a person do for the environment so the future can be approached with a benevolent attitude? How can we make people appreciate their environment better? With these values, I would try to increase my ecosophical attitude in elementary school, and I call that optimism. I believe that this approach is of great importance in elementary school eco-education. Namely, the mentality of sustainable eco-education does not, in my opinion, support such efforts where huge amounts of information are poured into the child’s developing thinking. There is no reason to pressure any student to be anxious about the environmental crisis. Instead, the effort is to help the students understand why changes need to be made. Humans are capable of better things; you have to believe in that. Above all, it is important to make the next generation realize that there is reason to believe in good. Then we will be able to fight for the diversity of nature, and we will hopefully look for more sustainable solutions!”
Critical and reflective knowledge appeared in approximately 5% of both FPSTs’ and SPSTs’ answers, focused on future perspectives, anxiety and threats, together with encouragement. SPST161 answered,
“In my opinion, one should not create big images of threats but rather encourage students to create solutions that are sustainable for the planet in their own everyday lives.”
Methodological and Metacognitive Content Knowledge of Key Environmental Problems Locally, Regionally and Globally
Evaluative, critical and reflective knowledge was barely found in the answers regarding environmental problems, above all, among Spanish student teachers.
Evaluative knowledge focused on someone’s own actions regarding local environmental problems. Concerning regional environmental problems, the focus was assessing one’s own competence, individual possibilities and results, means of action or evaluations of the problem’s magnitude. Respecting global environmental problems, the PSTs targeted an evaluation of the student’s knowledge level, the possibilities of influencing oneself, the company and responsibilities or evaluations of the influential possibilities. Thus, FPST169 wrote,
“Difficulties caused by overpopulation to curb climate change.”
Critical and reflective knowledge was also present in the answers regarding environmental problems. The PSTs focused locally on the critical examination of consumption habits. For example, SPST83 wrote the following:
“In my town, we have a chemical derivatives company that does not stop pouring toxic gases into the atmosphere, thus compromising the health of citizens and the species that live in this space. And all this for the economic interests of the company and the town council, which does nothing to change it. If inspections were carried out in a regulatory and regular manner, the health of citizens would not be compromised.”
Globally, criticism was directed at procedures, for example
“Large factories do not follow environmental laws or disposable consumption culture, which should be got rid of, difficult to solve because big polluters like China do not commit” (FPST126).
In answers related to regional problems, reflective knowledge focused on the inadequacy of one’s own knowledge, skills and activities and on reflecting on one’s opportunities for influence. For example, FPST99 wrote the following:
“Environmental problems in Finland include, for example the pollution of waterways, the reduction of biodiversity and littering. To solve these problems, the Finnish government should make policies that reduce the aforementioned disadvantages. I can influence things myself with my own choices and by voting for parties who promote the environment as state decision makers.”
DISCUSSION
This study focused on student teachers’ views of key questions, concepts and environmental issues and on their views of the teaching skills that should be taught biology and the geosciences. Previous research has shown that people’s ability to identify factors affecting ecological sustainability can be developed by supporting their understanding of SCK, such as core ecological concepts and processes (Palmberg et al., 2016) and a knowledge of teaching strategies and methods (Yli-Panula et al., 2017).
However, few studies have been conducted on the theoretical distinction between SCK and PCK as well as observations of their empirical distinctions (Kleickmann et al., 2013). This study contributes to the situation by clarifying what kind of student teachers’ SCK and PCK are, and what misconceptions and deficiencies they have regarding them. This information can be used as the basis for teacher education programs to further develop a sustainability pedagogy for biology teaching.
In the answers of the FPST and SPST, both SCK and PCK appeared. The most common knowledge was not only factual and conceptual, but also methodological and metacognitive, whereas critical reflections, reflective knowledge and evaluative knowledge appeared rarely in the answers. The previously mentioned factual and conceptual knowledge, for example climate issues, biodiversity and river pollution, has a strong basic connection to the natural sciences. However, they are also deeply connected to society and the economy. To solve these kinds of socio-scientific issues, the solver needs at least basic factual content knowledge in the natural sciences and, according to Roberts and Bybee (2014), skills to explain natural scientific phenomena such as the biodiversity mentioned by the PSTs.
In current education, both SCK and subject-specific PCK (Hudson et al., 2023) are considered essential for teaching. The purpose of science education is to define teaching according to how it considers the meaning of a subject and the possibility of its application to the external, real-world phenomena of the school (Roberts & Bybee, 2014). This also includes an understanding of the relationships between facts and concepts. Facts and concepts were often combined (i.e., incapable of separate analysis) in PSTs’ answers, which suggests that they did not necessarily master or know how to distinguish between the phenomenon itself, and the related concept. Student teachers must develop their scientific understanding of the latest key ecological concepts in teacher education to avoid spreading their own misconceptions as teachers.
The essential factual and conceptual knowledge mentioned by the PSTs to be taught in primary school was mainly connected to ecological sustainability, such as recycling or renewable natural resources, which represent real-world phenomena and can be regarded as knowledge about principles and generalizations. At the conceptual level, they also represent terminological knowledge after Shulman’s (1987) classification. These phenomena are also written in SCK in the Finnish and Spanish school curricula (FNBE, 2016; LOMLOE, 2020). The true real-world phenomenon in South Spain can be a lack of drinking water. It can be regarded as an important detail or basic element of sustainability issues and is not only based on ecology but also deeply connected to social environmental issues and represents so-called socio-scientific issues (Sadler, 2004). The factual and conceptual knowledge regarding key environmental problems (i.e., littering, recycling, pollution, plastic waste, global warming, and climate change) in the PSTs’ answers represented the powerful SCK (Young et al., 2014) regarding sustainability. For these authors, this kind of knowledge is empowering. With this knowledge, the learner can study ways of acting and participate in societal and ethical debates.
Roberts and Bybee (2014) describe ability in natural sciences education using the term scientific competence. This includes describing phenomena scientifically, and it always includes methodological knowledge skills. Because the phenomenon was not usually described but only listed as concepts, the PSTs did not demonstrate deep interpretation with scientifically competent answers. Especially when the methodological connection (in half of the answers) was missing, scientific competence appeared to be weak.
In general, factual and conceptual content knowledge intersect with ecological, social and economic sustainability (Yli-Panula et al., 2022), and it could be assumed to be seen in such facts presented by the PSTs. Their answers did not often include explanations of phenomena, so the PSTs did not demonstrate their scientific competence in connecting the issues they presented to these three areas of sustainable development. Student teachers may find it difficult to teach about sustainability and all its dimensions and aspects. They need training in SE, as suggested by many other studies (Borg et al., 2012; Uitto & Saloranta, 2017).
Metacognitive knowledge existed only in 10% of the PSTs’ answers, and evaluative knowledge seldom occurred in the answers. Roberts and Bybee (2014) connected this evaluative knowledge as an important ability, for example to research skills in biology and thus part of the powerful knowledge of the subject.
Critical and reflective knowledge rarely appeared in the PSTs’ answers. Only some PSTs emphasized the need to find sustainable solutions to environmental problems. Although factual knowledge is important (Puig & Jiménez-Aleixandre, 2022), critical thinking and the utilization of knowledge of biology and geosciences in everyday situations are essential when dealing with topics. Teaching critical thinking can support learners in recognizing how researched scientific knowledge differs from non-scientific or pseudoscientific claims, regarding, for example biodiversity loss or climate change (Hansson, 2021).
Most researchers and education policymakers emphasize that the slogan ‘scientific literacy for all citizens’ means not only a discipline-specific understanding of concepts and the nature of knowledge (Kapon et al., 2018; Roberts & Bybee, 2014) but also acquiring powerful knowledge (Young et al., 2014). Powerful knowledge is knowledge that help individuals understand and explain the world and gives them certain ‘powers’ in terms of capacity to move beyond their context-bound experience (Young, 2013; Young & Muller, 2013). It supports the empowerment of individuals and the transformation of their understanding to find not only reliable explanations for world phenomena but also new ways of perceiving the world. He or she can learn ways of doing things that enable participation in social and ethical debates (Young et al., 2014) about the implementation of sustainable development. Powerful knowledge promotes the future school, where sustainable knowledge has a central role in promoting social justice.
In biology education including SE, transformation of individuals’ understanding of sustainability can be supported by integrating different forms of knowledge into teaching and learning situations. In the context of sustainable development, knowledge can be categorized into evaluative, declarative (factual), schematic, procedural and strategic knowledge.
Evaluative knowledge includes issues from the individual level (micro level) to communities (meso level, schools, educational institutions) and societal institutions (macro level, cities, regions, states; Boeren, 2019). Using theory-based evaluation, educational practices can be developed and enhance and understanding among students and teachers can be enhanced (Seeber et al., 2019). Declarative knowledge, such as ecological principles, is crucial regarding sustainability (Michaelis, 2017). Schematic knowledge is used to describe what happens outside of our direct experience or perception. Declarative and schematic knowledge are crucial for understanding the different biological content areas and their applications in SE. Procedural knowledge comprises actions that are suitable for certain types of problems in the specific domain (de Jong & Ferguson-Hessler, 1996). For example, climate change is one of the teaching and learning topics which offer good opportunities for creativity and via creativity to support students’ problem-solving skills concerning environmental problems from local to global level. Decision-making situations require the integration of different types of knowledge. For example, management decision making requires the integration of declarative and procedural knowledge and the application of schematic and strategic knowledge (schematic [why] and strategic [when, where, how] knowledge) (Seeber et al., 2019).
For supporting sustainable behavior in biology education, it is crucial to emphasize systems thinking and focus interconnections between environmental, social and economic dimensions of sustainable development (Fischer et al., 2024). In addition, it is also important to apply transformative didactics to the learning of cultural perspectives.
CONCLUSION AND IMPLICATIONS
This study explored student teachers’ views of key teaching issues, concepts and environmental issues in biology and geosciences, as well as their views of the teaching skills that should be taught in these subjects. The PSTs demonstrated not only many strengths but also limitations in their views regarding SCK and knowledge of environmental teaching skills. Many PSTs considered it important to teach factual, conceptual, methodological and metacognitive knowledge and skills useful for solving local, regional and global environmental problems. They also presented critical and evaluative information, but quite rarely.
The results of the study suggest that some aspects of knowledge must be addressed to biology and geoscience teachers to be successful in teaching SCK and PCK and integrating biology and geosciences with environmental issues. First, student teachers must have the goals and purposes clear that focus on student learning with respect to scientific knowledge, scientific process skills and scientific attitudes. Second, strong SCK makes it easier for student teachers to teach SE through different teaching and learning methods. One of the goals of natural science education is to promote a breakthrough in sustainability and support children’s and young people’s growth in environmental responsibility. This means changes to the subjects of biology and geoscience. The role of teachers in this comprehensive support of sustainability skills is crucial. The role of education is emphasized especially in the current ‘post-truth’ era, where researched information mixes with opinions and in some reference groups the challenge is even dealing with science denial (Sinatra & Hofer, 2021). Questioning the status of researched information is not a new phenomenon. For example, in the case of biological information, its consequences have taken serious forms when people refuse to make (environmentally) responsible choices.
The main lesson of this study is related to Shulman’s (1986) framework. The slavish application of the framework can lead to the situation where certain epistemological assumptions about PCK can promote an understanding that reflects the features of the process-product research paradigm (Dunkin & Biddle, 1974)–and the behaviorism that influenced it–of which Shulman’s (1986) work was a timely and influential critique (Tallman, 2023).
Another challenge is that due to diverse traditions and cultural backgrounds, pedagogical approaches and teaching methods as context-dependent issues can vary between countries. Also, SE can be understood in different ways due to cultures and environmental factors across countries and educational institutions. In addition, language differences can pose challenges in research design and implementation. These things can also affect student teachers’ perceptions of SCK and understanding of PCK in biology education including SE.
As for the trustworthiness of the study (Elo et al., 2014), the design and implementation of the study was negotiated among the researchers throughout the research process. The study procedures were carefully documented to review and verify data throughout the study. The analysis of the data was carried out independently by three researchers. At the end of the analysis process, the researchers compared and discussed their classifications until a unified view was reached. The results were also compared with previous studies.
Due to the issues mentioned above, the results should be interpreted with caution. However, from a practical point of view, we hope that they will provide ideas for promoting a transformative approach and sustainability aspects in teaching to develop curricula and practices in teacher education and at schools.
Author contributions: EY-P, IB-G, EJ, & EM: study design, formal analyses, writing – original draft, writing – review & editing. All authors have agreed with the results and conclusions.
Funding: This work was supported by the Grant PID2019-105705RA-I00 funded by MCIN/AEI/10.13039/ 501100011033 and by the Moving Minds Program of the University of Murcia.
Ethical statement: The authors stated that they have carried out the study according to the ethical principles indicated by TENK (2019). Ethical approval number for the study is 3760/2022. Written informed consents were obtained from the participants.
AI statement: The authors stated that they have not used Generative AI or AI-based tools for the preparation of the manuscript.
Declaration of interest: No conflict of interest is declared by the authors.
Data sharing statement: Data supporting the findings and conclusions are available upon request from the corresponding author.
References
- Anderson, L. W., Krathwohl, D. R., Airasian, P. W., Cruikshank, K. A., Mayer, R. E., Pintrich, P. R., Raths, J., & Wittrock, M. C., Eds. (2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing. A revision of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives. Addison Wesley Longman.
- Blömeke, S., Gustafsson, J., & Shavelson, R. (2015). Beyond dichotomies: Competence viewed as a continuum. Zeitschrift für Psychologie, 223(1), 3-13. https://doi.org/10.1027/2151-2604/a000194
- Boeren, E. (2019). Understanding sustainable development goal (SDG) 4 on “quality education” from micro, meso and macro perspectives. International Review of Education, 65, 277-294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11159-019-09772-7
- Borg, C., Gericke, N., Höglund, H.-O., & Bergman, E. (2012). The barriers encountered by teachers implementing education for sustainable development: Discipline bound differences and teaching traditions. Research in Science & Technological Education, 30(2), 185-207. https://doi.org/10.1080/02635143.2012.699891
- Broncano, F. (2014). Daring to believe: Metacognition, epistemic agency, and reflective knowledge. In A. Fairweather (Ed.), Virtue epistemology naturalized: Bridges between virtue epistemology and philosophy of science (pp. 49-66). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-04672-3_4
- Burroughs, N., Gardner, J., Lee, Y., Guo, S., Touitou, I., Jansen, K., & Schmidt, W. (2019). A review of the literature on teacher effectiveness and student outcomes. In Teaching for excellence and equity. In N. Burroughs, J. Gardner, Y. Lee, S. Guo, I. Touitou, K. Jansen, & W. Schmidt (Eds.), Analyzing teacher characteristics, behaviors, and student outcomes with TIMSS. IEA research for education, vol 6 (pp. 7-17). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16151-4_2
- Cole, M. J. (2023). Evaluative thinking. Evaluation Journal of Australasia, 23(2), 70-90. https://doi.org/10.1177/1035719X231163932
- de Jong, T., & Ferguson-Hessler, M. G. M. (1996). Types and qualities of knowledge. Educational Psychologist, 31(2), 105-113. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15326985ep3102_2
- Dempster, E. R. (2023). What is ‘powerful knowledge’ in school biology? Journal of Biological Education57(2), 245-247. https://doi.org/10.1080/00219266.2023.2190269
- Dunkin, M. J., & Biddle, B. J. (1974). The study of teaching. Hold, Rinehart, & Winston.
- Elo, S., Kääriäinen, M., Kanste, O., Pölkki, T., Utriainen, K., & Kyngäs, H. (2014). Qualitative content analysis: A focus on trustworthiness. SAGE Open, 4(1). https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244014522633
- European Parliament. (2023). Environment policy: General principles and basic framework. European Parliament. https://www.europarl.europa.eu/erpl-app-public/factsheets/pdf/en/FTU_2.5.1.pdf
- Fischer, A., Havu-Nuutinen, S., Kontkanen, S., & Suortti, E. (2024). Investigating sustainability education in the science capital teaching approach: Competence development and pillar considerations. Interdisciplinary Journal of Environmental and Science Education, 20(4), Article e2418. https://doi.org/10.29333/ijese/15038
- Fitriah, E., Munadi, S., & Djukri. (2018). Understanding of pre-service biology teachers students toward pedagogical content knowledge (PCK). Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1097, Article 012041. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1097/1/012041
- FNBE. (2016). The national core curriculum for basic education. Finnish National Board of Education.
- García-Fortes, M. Á., Banos-González, I., & Esteve-Guirao, P. (2024). ESD action competencies of future teachers: Self-perception and competence profile analysis. International Journal of Sustainability in Higher Education, 25(8), 1558-1580. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJSHE-07-2023-0323
- Gudmundsdottir, S., & Shulman, L. S. (1987). Pedagogical content knowledge in social studies. Scandinavian Journal of Educational Research, 31(2), 59-70. https://doi.org/10.1080/0031383870310201
- Hansson, S. O. (2021). Science and pseudo-science. In E. N. Zalta (Ed.), The Stanford encyclopedia of philosophy.
- Hattie, J. (2011). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses related to achievement. International Review of Education, 57, 219-221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11159-011-9198-8
- Hudson, B., Gericke, N., Olin-Scheller, C., & Stolare, M. (2023). Trajectories of powerful knowledge and epistemic quality: Analysing the transformations from disciplines across school subjects. Journal of Curriculum Studies, 55(2), 119-137. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220272.2023.2182164
- Jeronen, E. (2023). Sustainable education. In S. O. Idowu, R. Schmidpeter, N. Capaldi, L. Zu, M. Del Baldo, & R. Abreu (Eds.), Encyclopedia of sustainable management(pp. 3488-3497). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25984-5_237
- Kapon, S., Laherto, A., & Levrini, O. (2018). Disciplinary authenticity and personal relevance in school science. Science Education, 102(5), 1077-1106. https://doi.org/10.1002/sce.21458
- Kleickmann, T., Richter, D., Kunter, M., Elsner, J., Besser, M., Krauss, S., & Baumert, J. (2013). Teachers’ content knowledge and pedagogical content knowledge: The role of structural differences in teacher education. Journal of Teacher Education, 64(1), 90-106. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022487112460398
- Kleickmann, T., Tröbst, S., Heinze, A., Bernholt, A., Rink, R., & Kunter, M. (2017). Teacher knowledge experiment: Conditions of the development of pedagogical content knowledge. In D. Leutner, J. Fleischer, J. Grünkorn, & E. Klieme (Eds.), Competence assessment in education, methodology of educational measurement and assessment (pp. 111-129). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-50030-0_8
- Koster, B., & Dengerink, J. (2008). Professional standards for teacher educators: How to deal with complexity, ownership, and function. Experiences from the Netherlands. European Journal of Teacher Education, 31(2), 135-149. https://doi.org/10.1080/02619760802000115
- Krathwohl, D. R. (2002). A revision of Bloom’s taxonomy: An overview. Theory into Practice, 41(4), 212-218. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15430421tip4104_2
- Krippendorff, K. (2013). Content analysis: An introduction to its methodology. SAGE.
- Laghari, M. A., Chachar, Z. A., & Bachal, S. (2023). An overview of the influence of teachers’ subject matter knowledge on students’ academic achievement. Journal of Academic Research for Humanities, 3(3), 252-258A.
- Landis, J. R., & Koch, G. G. (1977). An application of hierarchical kappa-type statistics in the assessment of majority agreement among multiple observers. Biometrics, 33(2), 363-374. https://doi.org/10.2307/2529786
- LOMLOE. (2020). Ley orgánica 3/2020, de 29 de Diciembre, por la que se modifica la ley orgánica 2/2006, de 3 de Mayo, de educación [Organic law 3/2020, of December 29, amending organic law 2/2006, of May 3, on education]. BOE, 340, 122868-122953.
- Lutovac, S., & Körkkö, M. (2024). ‘A teacher’s work is many things, but one thing it is not is easy’: Pre-service teachers’ conceptions of teachers’ work. European Journal of Teacher Education, 1-18. https://doi.org/10.1080/02619768.2024.2388630
- Metsäpelto, R.-L., Poikkeus, A.-M., Heikkilä, M., Husu, J., Laine, A., Lappalainen, K., Lähteenmäki, M., Mikkilä-Erdmann, M., Warinowski, A., Iiskala, T., Hangelin, S., Harmoinen, S., Holmström, A., Kyrö-Ämmälä, O., Lehesvuori, S., Mankki, V., & Suvilehto, P. (2022). A multidimensional adapted process model of teaching. Educational Assessment, Evaluation and Accountability, 34(2), 143-172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11092-021-09373-9
- Michaelis, C. (2017). Kompetenzentwicklung zum nachhaltigen Wirtschaften. Eine Längsschnittstudie in der kaufmännischen Ausbildung [Developing skills for sustainable business practices: A longitudinal study in commercial education.]. Peter-Lang. https://doi.org/10.3726/b10896
- Muller, J., & Young, M. (2019). Knowledge, power, and powerful knowledge re-visited. The Curriculum Journal, 30(2), 196-214. https://doi.org/10.1080/09585176.2019.1570292
- Newman, I. (2000). A conceptualization of mixed methods: A need for inductive/deductive approach to conducting research. In Proceedings of the Annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association. New Orleans, LA.
- OECD. (2021). OECD environmental performance reviews: Finland 2021. OECD Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1787/d73547b7-en
- Osborne, J., Rafanelli, S., & Kind, P. (2018). Toward a more coherent model for science education than the crosscutting concepts of the next generation science standards: The affordances of styles of reasoning. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 55(7), 962-981. https://doi.org/10.1002/ea.21460
- Palmberg, I., Berg, I., Jeronen, E., Kärkkäinen, S., Norrgård-Sillanpää, P., Persson, C., Vilkonis, R., & Yli-Panula, E. (2015). Nordic-Baltic student teachers’ identification of and interest in plant and animal species–The importance of species identification and biodiversity for sustainable development. Journal of Science Teacher Education, 26(6), 549-571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10972-015-9438-z
- Palmberg, I., Jonsson, G., Jeronen, E., & Yli-Panula, E. (2016). Blivande lärares uppfattningar och förståelse av baskunskap i ekologi i Danmark, Finland och Sverige [Prospective teachers’ perceptions and understanding of basic knowledge in ecology in Denmark, Finland and Sweden]. Nordic Studies in Science Education, 12(2), 197-217. https://doi.org/10.5617/nordina.2557
- Park, S., & Oliver, S. (2008). Revisiting the conceptualisation of pedagogical content knowledge (PCK): PCK as a conceptual tool to understand teachers as professionals. Research in Science Education, 38(3), 261-284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11165-007-9049-6
- Pintrich, P. R. (2002). The role of metacognitive knowledge in learning, teaching, and assessing. Theory into Practice, 41(4), 219-225. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15430421tip4104_3
- Prabakaran, M. (2020). Historical appropriation of epistemological values: A goal ahead for higher education. Higher Education for the Future, 7(1), 67-81. https://doi.org/10.1177/2347631119886416
- Puig, B., & Jiménez-Aleixandre, M. P. (2022). Critical thinking in biology and environmental education: Facing challenges in a post-truth world. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92006-7
- Roberts, D., & Bybee, R. (2014). Scientific literacy, science literacy, and science education. In N. G. Lederman, & S. K. Abell (Eds.), Handbook of research on science education, volume II (pp. 559-572). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203097267-38
- Rockström, J., & Sukhdev, P. (2016). The SDGs wedding cake. Stockholm Resilience Center. https://www.stockholmresilience.org/research/research-news/2016-06-14-how-food-connects-all-the-sdgs.html
- Rockström, J., Steffen, W., Noone, K., Persson, Å., Chapin III, F. S., Lambin, E. F., Lenton,T. M., Scheffer, M., Folke, C., Schellnhuber, H. J., Nykvist, B., de Wit, C. A., Hughes, T., van der Leeuw, S., Rodhe, H., Sörlin, S., Snyder, P. K., Costanza R., Scedin, ... Foley, J. A. (2009). A safe operating space for humanity. Nature, 461, 472-475. https://doi.org/10.1038/461472a
- Rodgers, C. (2002). Defining reflection: Another look at John Dewey and reflective thinking. The Teachers College Record, 104(4), 842-866. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9620.00181
- Rosenkränzer, F., Kramer, T., Hörsch, C., Schuler, S., & Rieß, W. (2016). Promoting student teachers’ content related knowledge in teaching systems thinking: Measuring effects of an intervention through evaluating a videotaped lesson. Higher Education Studies, 6(4), 156-169. https://doi.org/10.5539/hes.v6n4p156
- Sadler, T. D. (2004). Informal reasoning regarding socioscientific issues. A critical review of research. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 41(5), 513-536. https://doi.org/10.1002/tea.20009
- Sarkar, M., Gutierrez-Bucheli, L., Yip, S. Y., Lazarus, M., Wright, C., White, P. J., Ilic, D., Hiscox, T. J., & Berry, A. (2024). Pedagogical content knowledge (PCK) in higher education: A systematic scoping review. Teaching and Teacher Education, 144, Article 104608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2024.104608
- Schön, D. A. (1992). The reflective practitioner: How professionals think in action. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315237473
- Schwab, J. J. (1978). Science, curriculum and liberal education. University of Chicago Press.
- Seeber, S., Michaelis, C., Repp, A., Hartig, J., Aichele, C., Schumann, M., Anke, J. M., Dierkes, S., & Siepelmeyer, D. (2019). Assessment of competences in sustainability management: Analyses to the construct dimensionality. Zeitschrift für Pädagogische Psychologie, 33(2), 148-158. https://doi.org/10.1024/1010-0652/a000240
- Shulman, L. S. (1986). Those who understand: Knowledge growth in teaching. Educational Researcher, 15(2), 4-14. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X015002004
- Shulman, L. S. (1987). Knowledge and teaching: Foundations of the new reform. Harvard Educational Review, 57(1), 1-23. https://doi.org/10.17763/haer.57.1.j463w79r56455411
- Sinatra, G. M., & Hofer, B. K. (2021). Science denial: Why it happens and what to do about it. Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780190944681.001.0001
- Sjöström, J., & Eilks, I. (2018). Reconsidering different visions of scientific literacy and science education based on the concept of bildung. In Y. J. Dori, Z. R. Mevarech, & D. R. Baker (Eds.), Cognition, metacognition, and culture in STEM education. Innovations in science education and technology (pp. 65-88). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66659-4_4
- Sterling, S. (2001). Sustainable education: Re-visioning learning and change. Green Books.
- Sterling, S. (2008). Sustainable education–Towards a deep learning response to unsustainability. Policy & Practice. A Development Education Review, 6, 63-68. https://www.developmenteducationreview.com/issue/issue-6/sustainable-education-towards-deep-learning-response-unsustainability
- Tallman, M. A. (2023). What makes pedagogical content knowledge “pedagogical”? Reconnecting PCK to its Deweyan foundations. The Mathematics Educator, 31(1), 100-128. https://doi.org/10.63301/tme.v31i1.2852
- Tuomi, J., & Sarajärvi, A. (2018). Laadullinen tutkimus ja sisällönanalyysi [Qualitative research and content analysis]. Kustannusosakeyhtiö Tammi.
- Uitto, A., & Saloranta, S. (2017). Subject teachers as educators for sustainability: Survey study. Education Sciences, 7(1), Article 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci7010008
- Valverde-Pérez, M., Esteve-Guirao, P., & Banos-González, I. (2022). How do prospective teachers address pupils’ ideas during school practices? Educational Sciences, 12(11), Article 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12110783
- Yli-Panula, E., Jeronen, E., & Mäki, S. (2022). School culture promoting sustainability in student teachers’ views. Sustainability, 14(12), Article 7440. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127440
- Yli-Panula, E., Jeronen, E., Seiko-Ahlström, H., & Ruotsalainen, E. (2017). Important biological issues for elementary pupils–A study of elementary pre-service teachers’ conceptions. Nordic Studies in Science Education, 13(2), 180-196. https://doi.org/10.5617/nordina.2579
- Young, M., & Muller, J. 2013. On the powers of powerful knowledge. Review of Education, 1(3), 229-250. https://doi.org/10.1002/rev3.3017
- Young, M., Lambert, D., Roberts, C. R., & Roberts, M. (2014). Knowledge and the future school: Curriculum and social justice. Bloomsbury.
How to cite this article
APA
Yli-Panula, E., Banos-Gonzalez, I., Jeronen, E., & Matikainen, E. (2025). Student teachers’ views on content knowledge of environmental issues in biological and geoscience subject matters. Interdisciplinary Journal of Environmental and Science Education, 21(4), e2520. https://doi.org/10.29333/ijese/17442
Vancouver
Yli-Panula E, Banos-Gonzalez I, Jeronen E, Matikainen E. Student teachers’ views on content knowledge of environmental issues in biological and geoscience subject matters. INTERDISCIP J ENV SCI ED. 2025;21(4):e2520. https://doi.org/10.29333/ijese/17442
AMA
Yli-Panula E, Banos-Gonzalez I, Jeronen E, Matikainen E. Student teachers’ views on content knowledge of environmental issues in biological and geoscience subject matters. INTERDISCIP J ENV SCI ED. 2025;21(4), e2520. https://doi.org/10.29333/ijese/17442
Chicago
Yli-Panula, Eija, Isabel Banos-Gonzalez, Eila Jeronen, and Eila Matikainen. "Student teachers’ views on content knowledge of environmental issues in biological and geoscience subject matters". Interdisciplinary Journal of Environmental and Science Education 2025 21 no. 4 (2025): e2520. https://doi.org/10.29333/ijese/17442
Harvard
Yli-Panula, E., Banos-Gonzalez, I., Jeronen, E., and Matikainen, E. (2025). Student teachers’ views on content knowledge of environmental issues in biological and geoscience subject matters. Interdisciplinary Journal of Environmental and Science Education, 21(4), e2520. https://doi.org/10.29333/ijese/17442
MLA
Yli-Panula, Eija et al. "Student teachers’ views on content knowledge of environmental issues in biological and geoscience subject matters". Interdisciplinary Journal of Environmental and Science Education, vol. 21, no. 4, 2025, e2520. https://doi.org/10.29333/ijese/17442

 Full Text (PDF)
Full Text (PDF)